Have you ever wondered how snakes effortlessly glide and twist their way through the grass, trees, and water without seemingly having any support structure? The fascinating world of snake anatomy, particularly its skeletal system, has long been subject to myths and misconceptions.
In this blog post, we will explore the unique structure of a snake’s skeleton to answer the burning question: “Do snakes have bones?” Get ready to unravel some surprising facts about these often-misunderstood creatures that might just change your perception of them entirely.
Key Takeaways
- Snakes do have bones, but their skeletal structure is unique and different from other animals. They have elongated vertebrae connected with ribs, allowing for lateral undulation movement.
- Snake skeletons contain hundreds of tiny vertebrae that give them flexibility and maneuverability. Their skull bones are connected by flexible ligaments to permit expansion when swallowing large prey whole.
- While it may seem counterintuitive that such a slender creature could possess so many bones, this unusual skeletal structure is what makes snakes such masters of movement. Snakes’ bone structure allows them to move in ways other animals cannot and slither through tight spaces with ease.
Snake Anatomy And Skeletal System
Snakes have a unique anatomy that allows them to move without limbs, including a long and flexible body and specialized muscles, but they still have a skeletal system.
Explanation Of Snake’s Unique Anatomy
Snakes possess a unique anatomy that sets them apart from other animals, allowing them to be incredibly flexible and agile hunters. One of the key features contributing to their distinctiveness is their elongated body accompanied by an equally long tail.
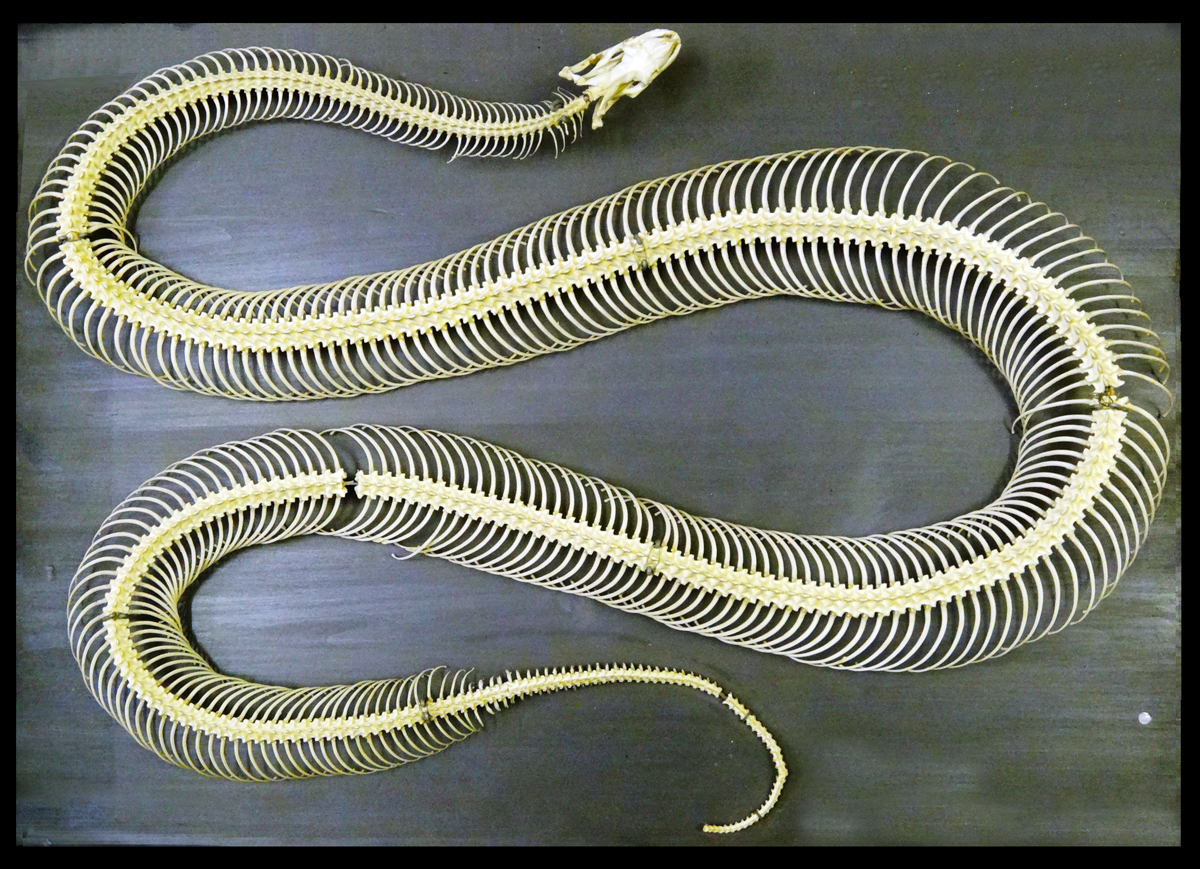
A closer look at the serpent’s intricate structure reveals that its backbone consists of numerous vertebrae connected with ribs, classifying snakes as vertebrates.
Interestingly, this elongated skeletal system has evolved independently in multiple reptilian and amphibian lineages – a concept known as convergent evolution among developmental biologists.
How Snakes Move Without Bones
At first glance, it may seem impossible for snakes to move without bones, given their fluid motions and incredible flexibility. However, the secret behind their movement lies in their unique skeletal system which consists of a long spine with up to 400 ribs attached.
Snakes employ a type of movement called lateral undulation – a serpentine action similar to the way fishes and eels swim. In this process, they push against objects or surfaces while contracting and expanding their muscles in rhythmic waves down their bodies.
This fascinating locomotion technique would not be possible without a highly specialized skeletal arrangement. Each vertebra is connected by strong yet flexible ligaments that allow for independent motion between individual bones, contributing significantly to a snake’s agility and dexterity during movement.
Do Snakes Have Bones?
Let’s clear up the misconception – snakes do have bones! In fact, their skeletons are more complex than you might think.
Clearing Up Common Misconceptions
One of the most prevalent misconceptions about snakes is that they lack bones due to their extraordinary flexibility and seemingly fluid movements. This mistaken belief likely stems from observing how these creatures effortlessly glide through various obstacles, twist into knots, and even constrict their prey with ease.
To further bust this myth, let’s delve into an example: the snake’s ability to swallow large prey whole. For humans and other animals with rigid bone structures, such feats would be impossible.
However, snakes possess highly specialized skull bones connected by flexible ligaments which permit expansion for consuming sizable meals without any hindrance.
Additionally, they have numerous vertebrae – significantly more than found in mammals – each one carefully designed and equipped with ribs necessary for both support and movement.
Explanation Of Snake’s Bone Structure
Snakes do have bones, but their structure varies significantly from other animals. Most of a snake’s skeleton is made up of its skull, spine, and ribs.
These tiny vertebrae allow snakes to move with incredible precision and speed. They also allow for the characteristic undulating movement seen in most snakes. Additionally, snakes’ ribs are not attached to the sternum like they are in other animals; instead, they attach only to each individual vertebra.
Overall, while snakes may seem like boneless creatures due to their slim bodies and remarkable contortion abilities, they do indeed have bones – just differently structured ones than we’re used to seeing in other animals.
The Surprising Answer
The surprising answer is that yes, snakes do have bones, but their bone structure is different from other animals, allowing them to move in their unique slithering motion.
Yes, Snakes Do Have Bones, Albeit Differently Structured Than Other Animals.
Snakes have a unique bone structure that enables them to be flexible and move in ways other animals cannot. Unlike humans, who typically have 33 vertebrae in their spine, some snake species can have up to 400 vertebrae.
Additionally, instead of having solid bones like most creatures do, snakes’ bones are hollow and extremely thin, providing greater flexibility. This unique design allows the snake to easily contort its body into various positions and slither through tight spaces with ease.
Conclusion 💭
In conclusion, the answer to whether snakes have bones is a resounding yes. Although their skeletons may be different than what we are used to seeing in other animals, they still contain hundreds of bones that play an essential role in their unique movement and survival strategies.
It’s fascinating how the evolution of snake anatomy has allowed them to adapt and thrive without limbs, relying on specialized backbones and ribs instead.
FAQs:
Do snakes have bones in their bodies?
Yes, snakes do have bones in their bodies but they are different from the typical mammalian skeletal system you may be familiar with. Snakes have a long and flexible backbone made up of numerous vertebrae that allow them to twist and contort their bodies easily.
How do snake bones differ from those of other animals?
Unlike most animals, snakes’ rib bones are not connected to their sternum, which allows for greater flexibility when moving and swallowing prey whole. Additionally, some species of snakes even have vestigial hip and leg bones within their skeletal structure.
Can snake bone structures vary between species?
Yes, the number of vertebrae present in a snake’s spine can vary significantly depending on the species. Some smaller snake species may only have around 100 vertebral segments while larger python or anaconda specimens can possess up to 400-500 individual pieces.
Why is it important to understand snake bone anatomy?
Understanding the anatomical features that make up a snake’s body helps researchers better comprehend how these animals move about and function in various environments across the globe. It also provides insight into how different adaptations lend themselves to survival tactics like hunting techniques or defense mechanisms used by particular species




Leave a Reply